This tool is aimed at identifying miRNAs that can be inhibited by user-submitted antisense sequences involves integrating dynamic programming algorithms with large sequence databases. The tool accepts RNA or DNA sequences from users, which are then processed to determine their complementarity with known miRNAs stored in a comprehensive database, such as miRBase. The underlying algorithm is based on the Needleman-Wunsch dynamic programming algorithm, traditionally used for global sequence alignment. This algorithm computes an optimal alignment by scoring matches, mismatches, and gaps between the user’s antisense sequence and target miRNA sequences. The scoring function is given by:
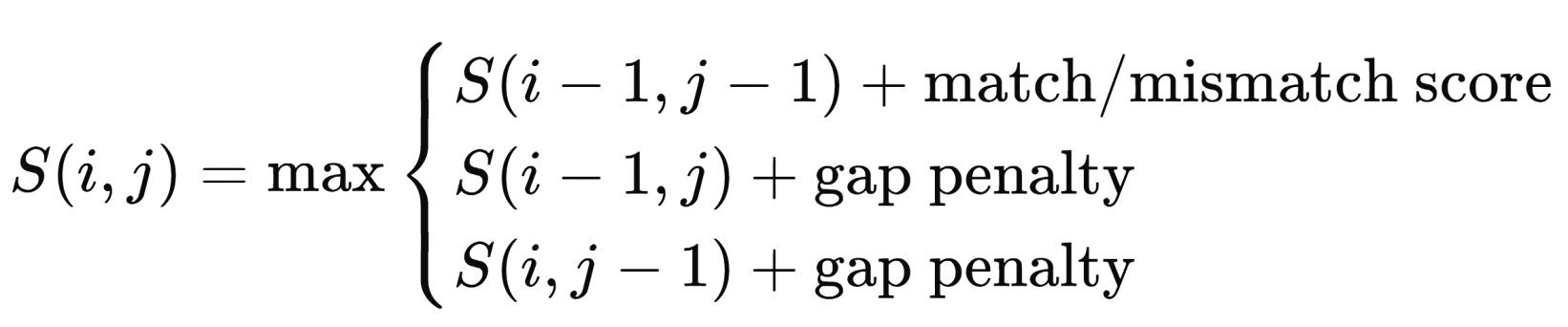
Where S(i,j); represents the alignment score between the ith base of the user sequence and the jth base of the miRNA sequence.
A match contributes a positive score, while mismatches and gaps incur penalties. Once the alignment is completed, the tool identifies miRNAs with the highest scores, indicating strong complementarity and potential for inhibition by the supplied antisense oligonucleotide. The tool also employs thermodynamic stability checks, considering binding energy (ΔG) to predict the likelihood of successful inhibition. This platform offers researchers a robust and efficient method for validating antisense oligonucleotides with high target specificity (Ganguli et al., 2011).